Written Language Production | PARAGRAPH STRUCTURE
Available
Written Language Production | PARAGRAPH STRUCTURE - is backordered and will ship as soon as it is back in stock.
Description
Description
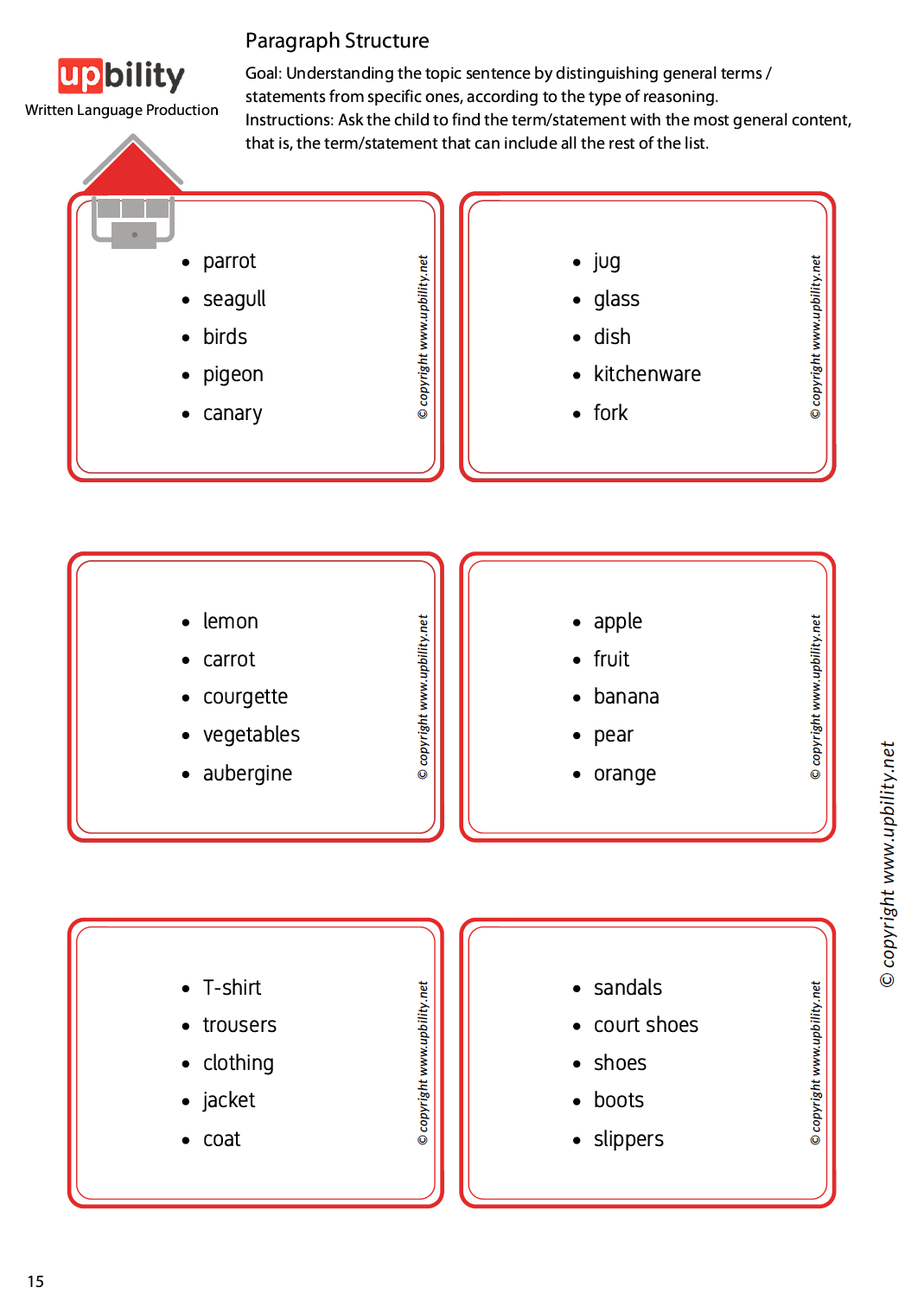
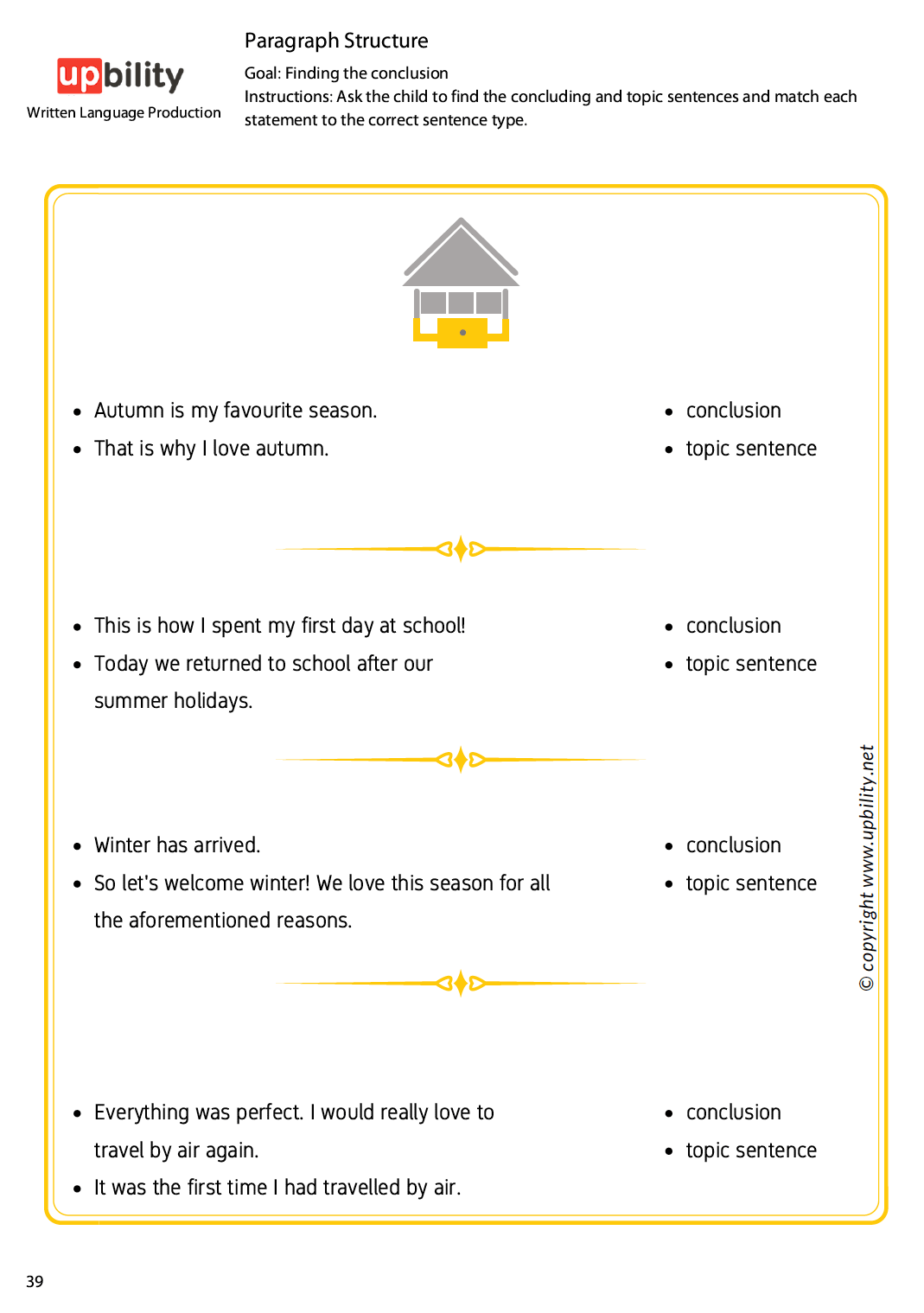
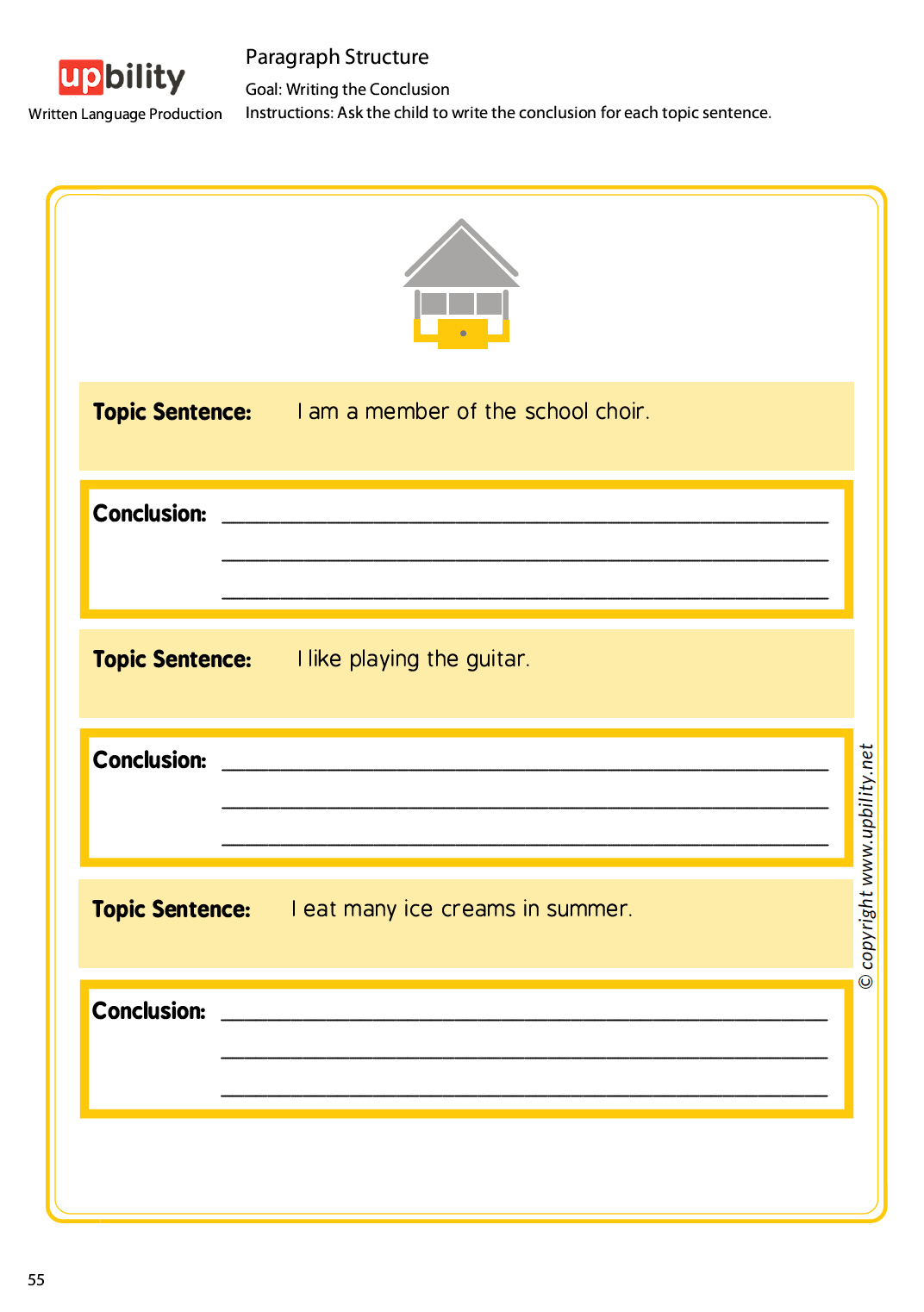
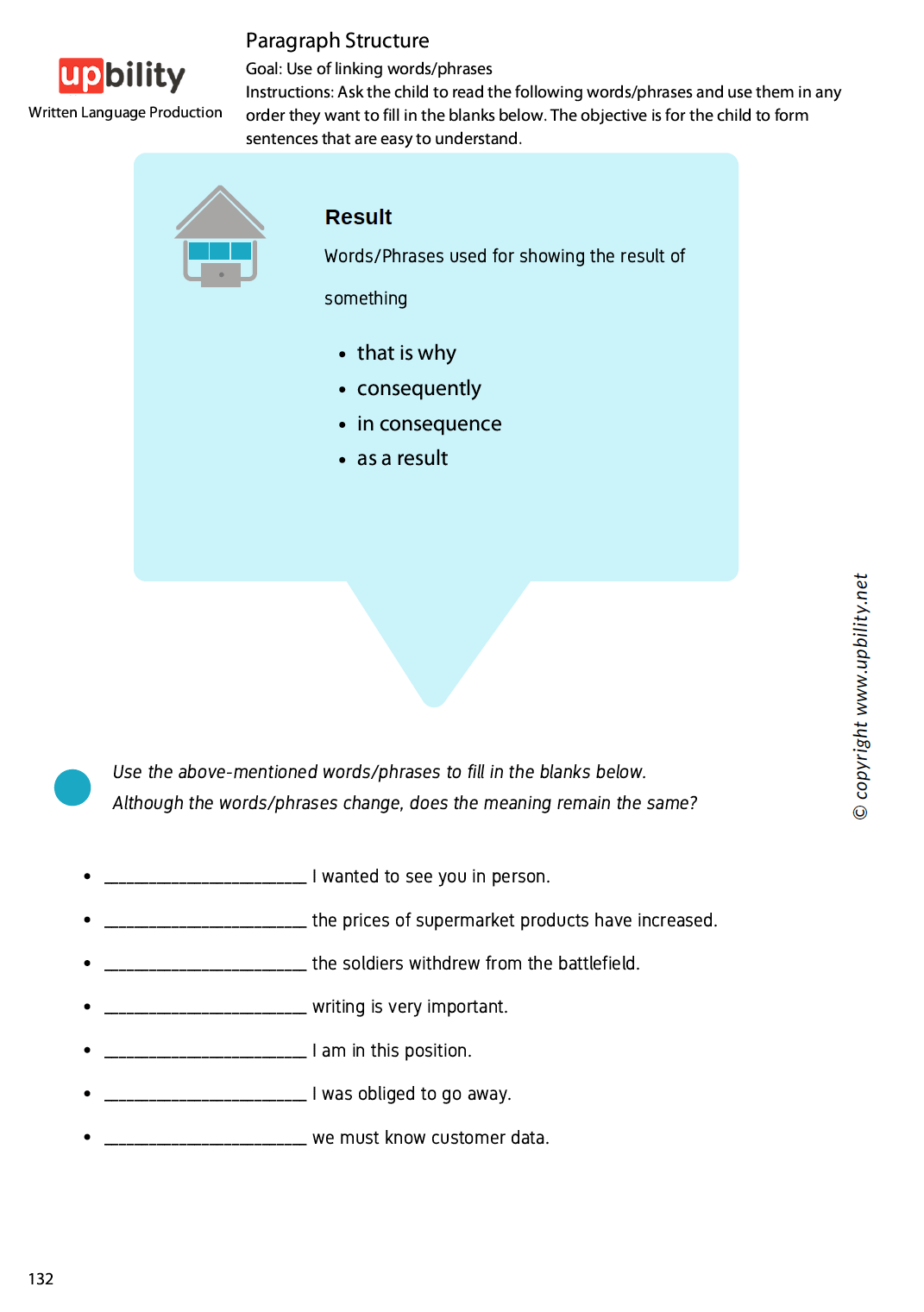
Paragraph Structure
Age Group : 7+
The first part is divided into three stages and nine levels, while the second one proposes ten strategies for guiding children towards paragraph development.
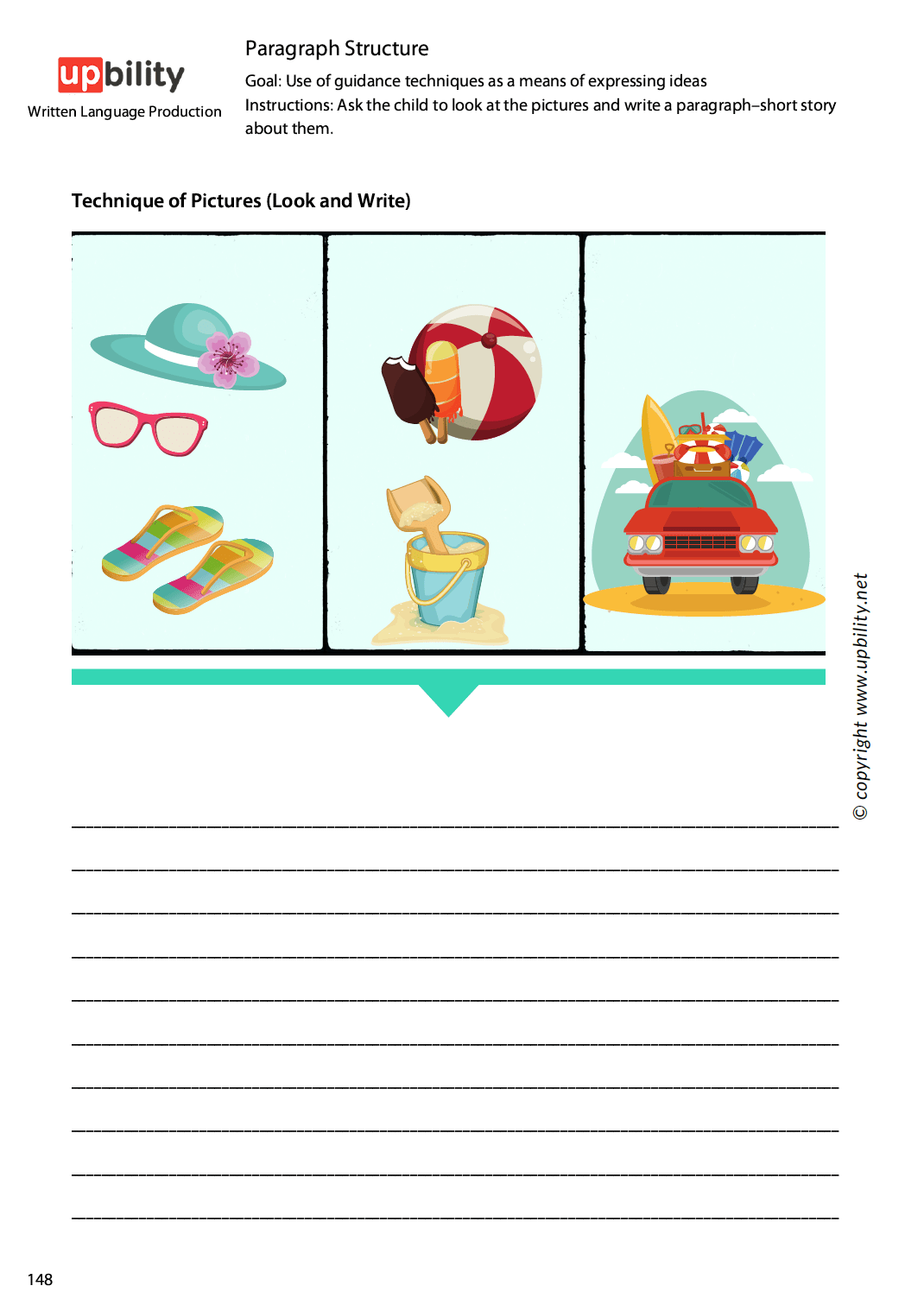
- Technique of Pictures (Look and Write)
- Technique of Modifying and Reversing Patterns
- Technique of Letters
- Technique of the Seven Questions (who, what, where, when, how, why, how much/long/often)
- Technique of Text Superstructures
- Technique of Incomplete Phrases and Phrases out of Logical Order
- Technique of Related Words
- Technique of Written Instructions
- Technique of the Fantastic Binomial
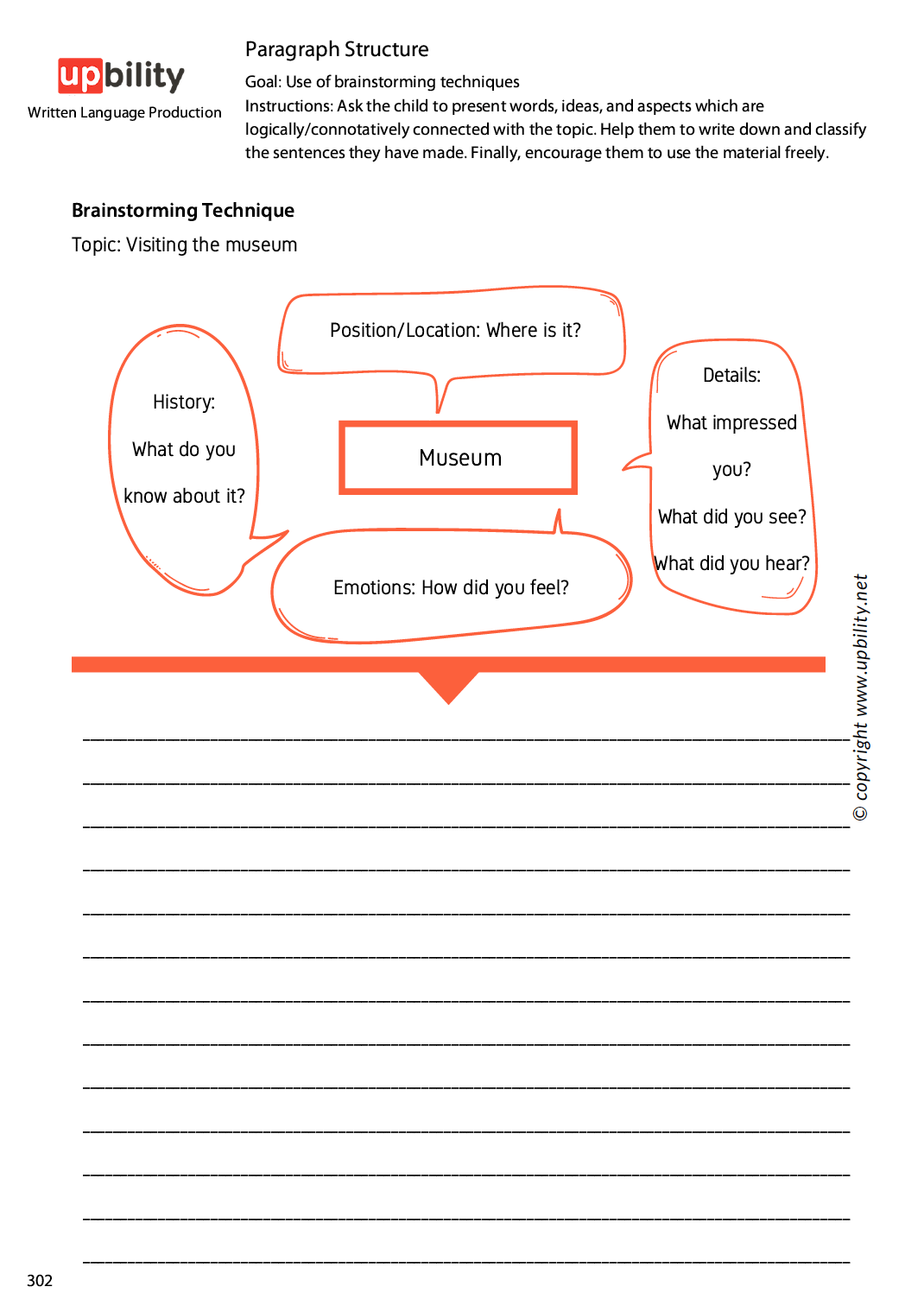
- Brainstorming Technique
Oral and Written Language
Language can be oral and written. It requires the operation of complex mechanisms. Oral language includes listening and speaking, while written language reading and writing.
Speaking/listening and writing/reading constitute the two fundamental means of language production and perception. Oral language is direct and has many paralinguistic features, including tone of voice, eye contact, style, body posture, and gestures. Paralinguistic elements of communication play an important role in how meaning is conveyed, helping listeners interpret content appropriately (Barton). On the other hand, written language lacks all the above-mentioned paralinguistic features. It is not direct and does not encourage feedback (Barton).
Check also the book "Written Language Production | SENTENCE STRUCTURE".
Specifications
Specifications
-
Book format
-
SKU
-
Age
-
Number of pages
-
Dimensions
-
Author
-
Pagination
-
Translation & Proofreading
-
Year of publication
Contents
Contents
Author
Author
Age
School-aged children
Author
Alice Kassotaki - Speech Language Pathologist MSc, BSc
Secure Payments
All major methods accepted — fully protected from checkout to delivery.